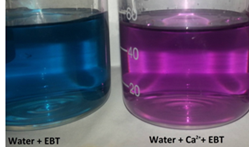
From where alkalinity comes in water?
The alkalinity of water is primarily a result of dissolved minerals, such as calcium, magnesium, and sodium carbonates and bicarbonates. These minerals can originate from geological sources, such as the dissolution of limestone or dolomite rocks, or from human activities like agriculture and industrial processes. Alkalinity is expressed in terms of equivalents of calcium carbonate … Read more